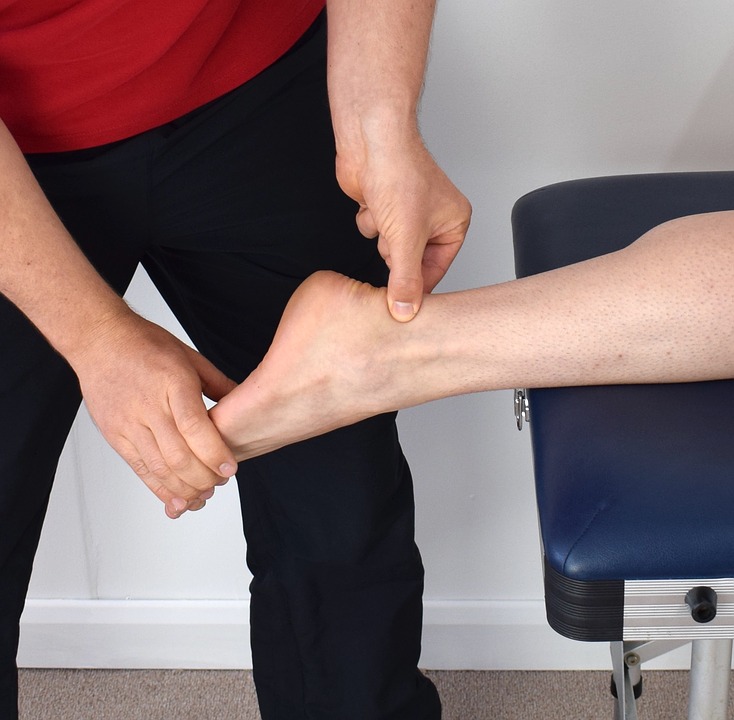
Achilles tendon tendinopathy is one of the most frequent injuries in running sports. The load will be a key element when it comes to an injury, as it happens in other tendinous structures. Overload, as well as an inadequate load adaptation, lack of load or sedentary life, will be risk factors to consider in this kind of injuries.
The Achilles tendon, just like other tendons, has the following main functions:
• transmission of power generated during muscle contraction.
• and the “spring effect”; which is, the uptake of part of the energy that is produced when the footsteps on the ground and the release of this energy in order to start an efficient and effective walk.
Even though the Achilles tendon is one of the most voluminous and powerful tendons of the human body, it is also prone to injuries.
We will talk about the Achilles tendon and how to prevent and treat the Achilles tendinopathy guided by Javier Herraiz, EPTE®’s Teaching, and Research Coordinator, in this post.
We should remember that the term tendonitis is not the most suitable as we are not talking about an inflammation per se as we usually refer to in a tendinopathy, but it is a term widely known and used.
Achilles tendon tendinopathy, what is it and why does it appear
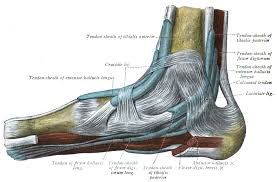 The Achilles tendon is the longest and one of the most powerful of the body. It is the tendinous continuity of the sural triceps, which is formed by the internal and external calf and the soleus. It inserts in the calcaneus by its distal part, located slightly lateral in the insertion and its fibres differently distributed with regard to the tendon typology. It helps to bear the weight of the human body and the stress it stands significantly increases when running, jumping and dancing. In such cases, the Achilles tendon bears eight to ten times higher weight of the human body.
The Achilles tendon is the longest and one of the most powerful of the body. It is the tendinous continuity of the sural triceps, which is formed by the internal and external calf and the soleus. It inserts in the calcaneus by its distal part, located slightly lateral in the insertion and its fibres differently distributed with regard to the tendon typology. It helps to bear the weight of the human body and the stress it stands significantly increases when running, jumping and dancing. In such cases, the Achilles tendon bears eight to ten times higher weight of the human body.
Generally, Achilles tendinopathies can be observed in two different locations. One of them is right at the bone attachment (Achilles enthesopathy, including not only the damage at the crossover from the tendon to the bone but also the dysfunction of the bursal recess), and the other one is in the tendon body, including the damage at the paratenon and at the tendon body itself.
Achilles tendon tendinopathy causes
 As set out at the beginning of the post, one of the main causes of the injury is the inadequate load adaptation. An overload, as well as the lack of load, will be risk factors to bear in mind. There are diverse intrinsic factors we should consider that may influence when there is an injury: a bad general conditioning to the activity that the patient needs to carry out due to an inadequate muscle function, motor control loss, lack of elasticity, a decrease in joint mobility, etc…
As set out at the beginning of the post, one of the main causes of the injury is the inadequate load adaptation. An overload, as well as the lack of load, will be risk factors to bear in mind. There are diverse intrinsic factors we should consider that may influence when there is an injury: a bad general conditioning to the activity that the patient needs to carry out due to an inadequate muscle function, motor control loss, lack of elasticity, a decrease in joint mobility, etc…
There are also other intrinsic factors like the body mass index, alterations in the lipid profile or diabetes that may increase the risk of suffering an Achilles tendinopathy, as well as some genetic factors that may influence this injury.
Achilles tendon tendinopathy treatment
Pain is one of the clearest signs of the Achilles tendontendinopathy, as well as the loss of function or functional impairment. This pain is a local pain of mechanical characteristics, occasionally related to morning stiffness, which may improve or not with motion activation depending on the evolutionary stage of the injury.
When treating Achilles tendinopathy it is crucial to perform a correct differential diagnosis. Orthopedic tests may help us, just as imaging tests that we must correlate with patient symptomatology findings because structural changes will be just one of the risk factors associated with the onset of the injury. Before treatment begins, we must follow a correct clinical reasoning that will establish the several evolutionary stages to follow during treatment.
To state, the evolutionary stage of the patient is essential, as well as determining the location of the injury along with the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that may worsen the injury. If the patient is in the reactive stage, marked by pain and functional impotence, our first goal should be load modulation and pain decrease. Once this phase has been overcome and depending on the physiotherapy diagnosis, we can apply various techniques available for health professionals.
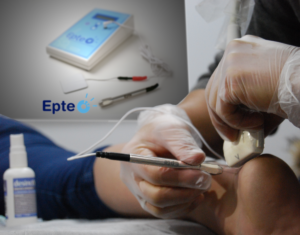 Generally, a tendinopathy comes with changes in the own tendon structure, a loss in muscle function and motor control. When talking about how to face structural and metabolic changes in the tendon, electrolysis is a tool of particular interest. EPTE® percutaneous electrolysis therapy technique is safe, effective and virtually painless. Moreover, patients’ recovery time is significantly reduced, allowing patients to return to their normal activity and introducing a load modulation program earlier.
Generally, a tendinopathy comes with changes in the own tendon structure, a loss in muscle function and motor control. When talking about how to face structural and metabolic changes in the tendon, electrolysis is a tool of particular interest. EPTE® percutaneous electrolysis therapy technique is safe, effective and virtually painless. Moreover, patients’ recovery time is significantly reduced, allowing patients to return to their normal activity and introducing a load modulation program earlier.
Before, during or after the electrolysis treatment, therapeutic exercisebecomes essential. There are different kind of exercises that professionals can recommend depending on their patient needs. The initial premise is the load modulation, with reduced speed, increasing loading gradually, to reach a final stage high-intensity stimuli and a speed-focused to the patients’ regular activity.
We need to remember that we always must visit a health professional who will set the most suitable treatment for this kind of tendon injuries.
We also recommend you these articles:
http://www.electrolisisterapeutica.com/en/tendon-injuries-tendinitis-treatment/
http://www.electrolisisterapeutica.com/en/biased-clinical-trials-negative-impact-for-the-physiotherapy-field/